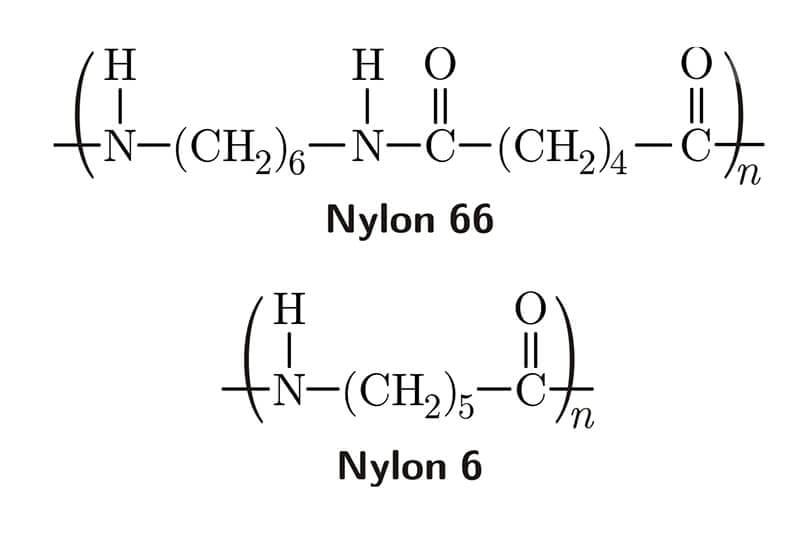
Polypropylene Vs. Polycarbonate: Comparing Properties and Applications

Polypropylene is widely known as “PP.” It is a thermoplastic polymer with exceptional mechanical and chemical properties. Its base material is propylene monomers. On the other hand, Polycarbonate’s short form is “PC.” It is renowned as a high-performance and transparent thermoplastic. This construction material’s base is bisphenol A monomer and phosgene.
Both of the materials are unique in terms of accommodating properties and offered advantages. Understanding Polypropylene vs Polycarbonate is essential for engineers and designers to select materials for specific applications while embracing cost-effectiveness. Here, we elaborate on the differences while covering some relevant aspects.
Polypropylene: Everything You Need to Know
Polypropylene was originated in 1954 by two Italian chemists named Giulio Natta and Karl Ziegler. They discovered the polymerization process of propylene, utilizing another remarkable invention called “catalysts.” This titanium-based catalyst was developed by Karl Ziegler. Due to their massive contribution to the industrial world and science, Natta and Ziegler received the Nobel Prize in 1963.
However, the production of Polypropylene is complex polymerization. In this process, propylene gas is carefully processed in the presence of either a Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalyst. Here, the influential factors such as temperature, reaction rate, and pressure are meticulously controlled to achieve the desired grade and quality of Polypropylene.
Common Characteristics of Polypropylene
In this section, we list the base characteristics of Polypropylene.
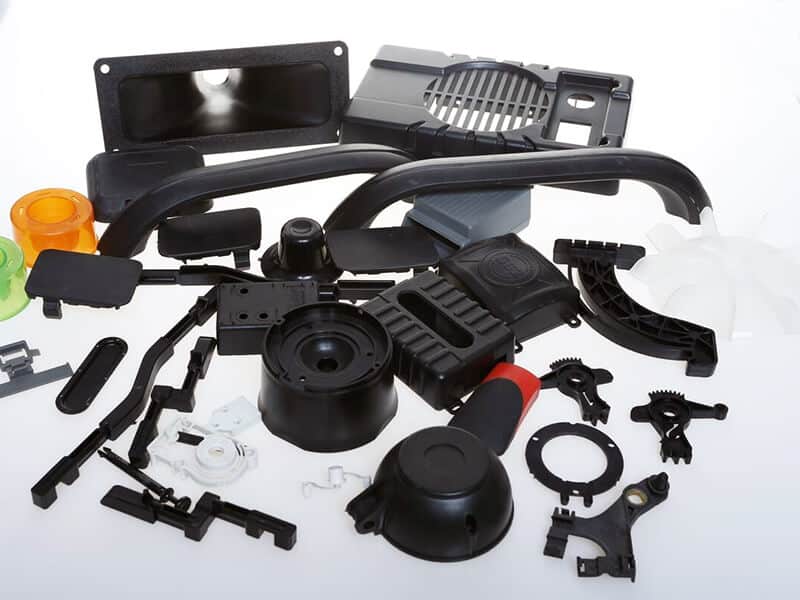
Common Applications of Polypropylene
Below is a comprehensive list of Polypropylene applications in various industries.
Advantages of Polypropylene
Here, we inform you of the advantages of Polypropylene use.
Disadvantages of Polypropylene
Below are the cons of Polypropylene.
Polycarbonate: Everything You Need to Know
The origination of polycarbonate is a little bit dramatic, consisting of three phases. First, Polycarbonate was initially invented by Dr. Hermann Schnell in 1953 while working on the development process of wire insulation material. Second, one week after the discovery by Schnell, another German scientist Dr. Daniel Fox also invented this material separately. But for some reason, the commercial production of this material did not happen till 1955. In 1955, GE and Bayer filed for US-based patents in the USA.
The production of Polycarbonate includes an interfacial process. In this process, bisphenol-A reacts with carbonyl chloride. Here, bisphenol-A is obtained from condensation of phenol and acetone under acidic conditions. The resulting bisphenol-A then undergoes a chemical reaction with carbonyl chloride to produce Polycarbonate.
Common Characteristics of Polycarbonate
In this section, we list the must-know characteristics of Polycarbonate.
Common Applications of Polycarbonate
Below are the uses of this material.
Advantages of Polycarbonate
Here are some crucial benefits of using Polycarbonate.
Disadvantages of Polycarbonate
The following are the problems associated with Polycarbonate.
Comparison Between Polypropylene Vs. Polycarbonate
| Type | Polypropylene | Polycarbonate |
|---|---|---|
| Short description | Polypropylene is a thermoplastic polymer | Polycarbonate is a high-performance and transparent thermoplastic |
| What ingredients used to make this | Propylene gas, Ziegler-Natta or metallocene catalyst | Bisphenol-A, carbonyl chloride |
| Applications | Polypropylene is used to manufacture car parts, geotextiles, outdoor furniture, pipes, storage boxes, etc. | Lenses, sunglasses, sunroofs, face shields, helmets, etc. |
| Characteristics | It can deal with extreme temperatures. Semi-rigid. Low-density. Recyclable. | Impact resistance. Lightweight, tough, stiff, and strong. Easy to fabricate. |
| Trade Name | Proteus, Propylux, etc. | Cyrolon, Lexan, Markrolon, etc. |
| Price | Per Ton Polypropylene price ranges from $1,850 to $2,550 | Per Ton price is $2,818 to $3,200. |
Final Words
Polypropylene and Polycarbonate are both thermoplastic materials, but they offer different properties. Polypropylene is a white opaque plastic that offers excellent chemical resistance; therefore, it is used for some tanks in corrosive environments. Polycarbonate is a transparent material, it is used frequently for machine shields, glass, etc.
If you are unfamiliar with polypropylene and polycarbonate plastic and need a trustworthy supplier, don’t hesitate to contact UVTECO, a leading supplier of plastic engineering and machining services.
Related Blogs

Looking for a trustworthy Supplier
Need a Trustworthy Supplier of Plastic, Foam, Sponge, Rubber, Metal, and Machining Solution. Click the Button, We Will Be In Touch With You As Quickly As Possible.