Key Factors to Consider When Choosing PVDF for Your Project
Learn the key considerations for selecting PVDF, including its performance in harsh environments, long-term durability, and suitability for your specific needs.

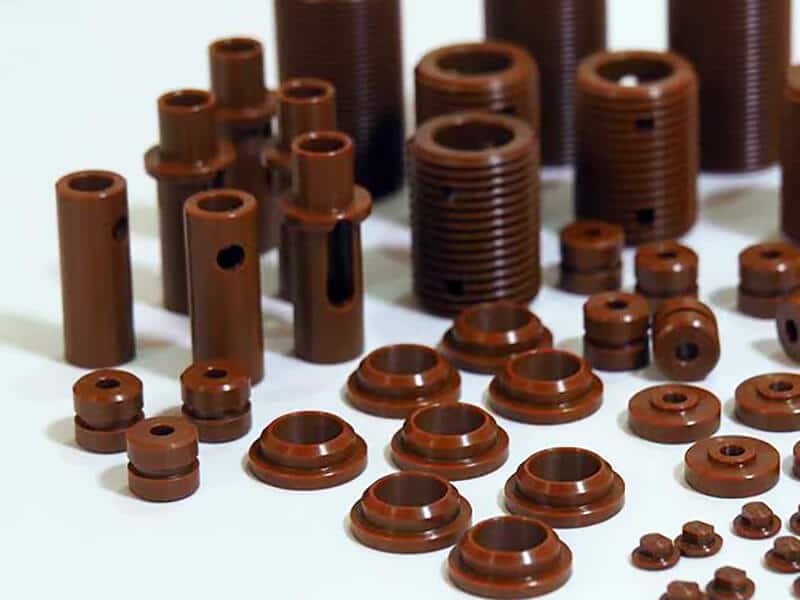
PVDF, also known as Polyvinylidene fluoride, is a highly versatile thermoplastic polymer. It is highly popular with manufacturers for its chemically inert nature and high resistance to hydrolysis. Its usability also includes its high level of thermal stability, excellent mechanical strength, and associated long-term performance.
These superior properties of PVDF, along with greater durability, weatherability, and processability, allow manufacturers to use it in industries like aerospace, healthcare, construction, etc.
However, using this construction material in every case is not wise or logical. Here are the key factors to consider when choosing PVDF for your project.
Basics of PVDF
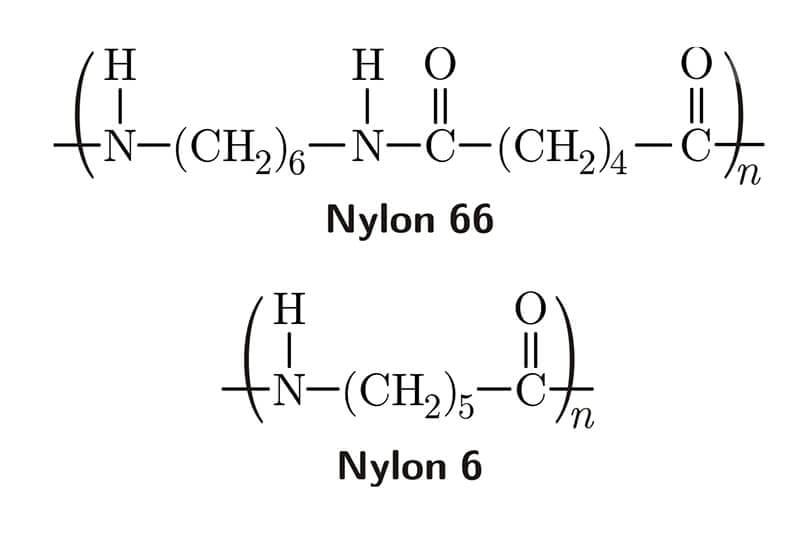
Polyvinylidene fluoride or PVDF is a durable construction material. Its base chemical is vinylidene fluoride and it offers high chemical resistance plus favorable stability. Let’s explore some crucial details about this construction material.
Production Process
As mentioned earlier, PVDF’s base chemical is vinylidene fluoride which is extracted from chlorodifluoromethane or other similar hydrocarbons. Now, a free-radical initiator triggers emulsion polymerization, starting a chain reaction towards forming a long chain of PVDF.
Here, PVDF’s properties, such as molecular weight, crystallinity, etc., are adjusted by controlling temperature, pressure, type of initiator, etc. Finally, processing steps such as coagulation, filtration, and drying of raw PVDF take place to make it ready for factory use.
Base Properties of PVDF
Most Common Applications of PVDF
7 Key Factors to Consider PVDF for Your Project
The following are the most important factors that one must consider before deciding on using PVDF.
1. Thermal Issues
Even though the thermal stability of PVDF is 150°C to 175°C and can retain some base properties at a temperature of 400°C, the temperature of the functioning environment must be evaluated.
Suppose the temperature does not fall within the suitable range for PVDF. In that case, a manufacturer needs to select other materials that can tolerate extremely low or high temperatures in comparison to PVDF’s thermal properties.
2. Mechanical Strength
PVDF has remarkable mechanical strength and can withstand a higher value of high mechanical loads, impacts, and vibrations. Still before using PVDF in any assembly like piping, fixing, etc. the possible orientation of mechanical stress must be assessed carefully.
Otherwise, for the first few days, the respective assembly with PVDF components will perform well but after some days the whole or partial portion of the assembly will be damaged.
3. Chemical Resistance
Certainly, PVDF is highly capable of resisting any reaction and breakdown in the presence of strong acids, bases, solvents, etc. However, it is not resistant to all harsh chemicals, such as aromatic hydrocarbons and ketones.
So, manufacturers must evaluate the properties of the chemicals in which the respective PVDF parts or PVDF-made components of a part will function.
4. Environmental Factor
PVDF is superbly resistive against UV light and weathering measures. These characteristics make Polyvinylidene fluoride a highly suitable construction material for the outdoor environment.
Still, there are different grades of PVDF and different UV plus weathering factors. For greater durability, the manufacturer, product designers, and users must assess these factors before using a particular grade of PVDF in comparison with the UV-strength and weathering factors’ level..
5. Cost
In general, PVDF plastic is more expensive than similar types of plastic or construction materials. Depending on the grades, the price per ton ranges from $4,900 to $12,600.
Here, the manufacturer, designer, and client must work together to find out whether the use of PVDF will be beneficial or not in comparison to other construction materials that can provide the same outputs.
6. Processing
In every manufacturing industry, professionals prefer using base materials that are easy to process and incorporate a higher degree of machinability. Even though the processing of PVDF is easy, the manufacturer must ensure that the processing of the respective PVDF as a base material is easy. It is also essential that PVDF is compatible with every prominent type of machining.
7. Sustainability
With the growing awareness regarding climate change, there are pressures on industries to use environmentally sustainable materials. Here, the use of PVDF in making a full part or part’s components is considered good due to its recyclability. Also, low energy consumption during production is a favorable factor.
Which One You Need: Expert Suggestions
The following table is designated to inform when to use PVDF Plastic.
| Criteria | Details |
|---|---|
| Harsh environment | It can use as electrical insulation |
| Fire resistant | If the PVDF is in reaction and the other chemicals used are very strong |
| Electrical application | When lightweight construction material with high fire and chemical resistance is needed, low-weight PVDF is needed. |
| Weight | When lightweight construction material is needed with high fire and chemical resistance, low-weight PVDF is needed. |
End Talks
We are sure that now our readers have a better understanding of the key factors to consider when choosing PVDF for your project is easy. By following the elaborations on the listed seven points, one can decide on go or no-go very quickly.
Finally, to decide whether to go with PVDF or not, a person must have a solid knowledge of PVDF and its criteria. If you don’t know PVDF very well but need some PVDF parts, contact UVTECO now. We are a trustworthy supplier of PVDF parts for your project.
Related Blogs

Looking for a trustworthy Supplier
Need a Trustworthy Supplier of Plastic, Foam, Sponge, Rubber, Metal, and Machining Solution. Click the Button, We Will Be In Touch With You As Quickly As Possible.