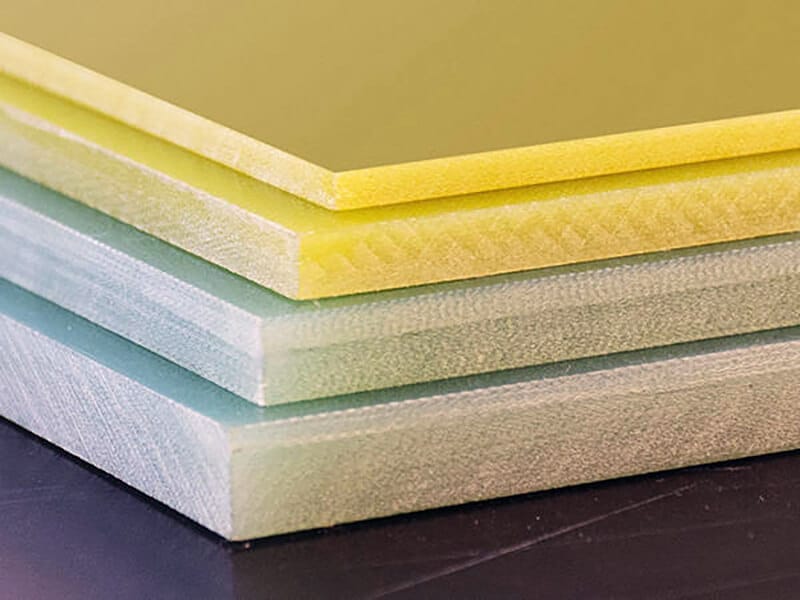
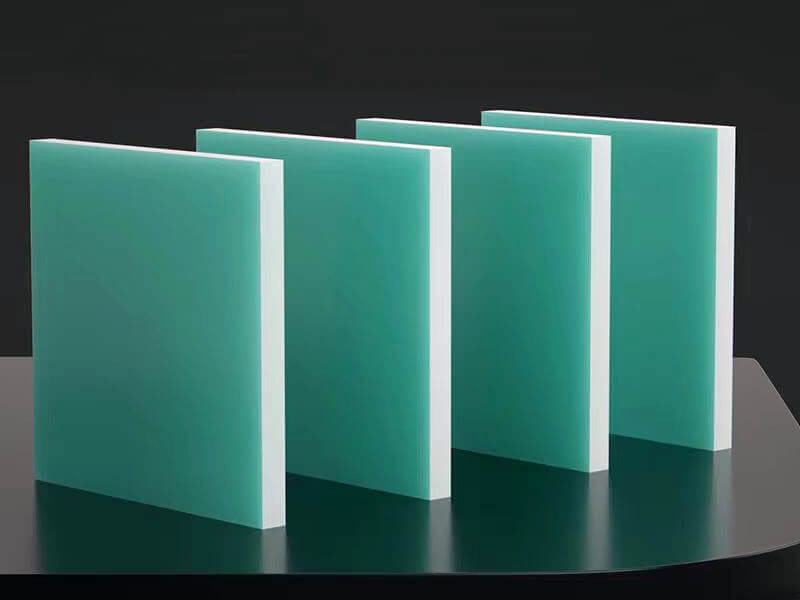
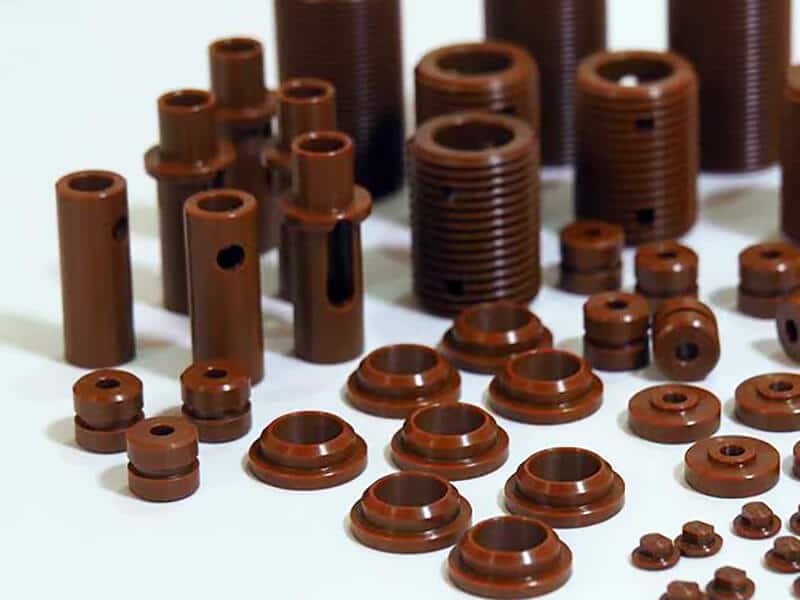
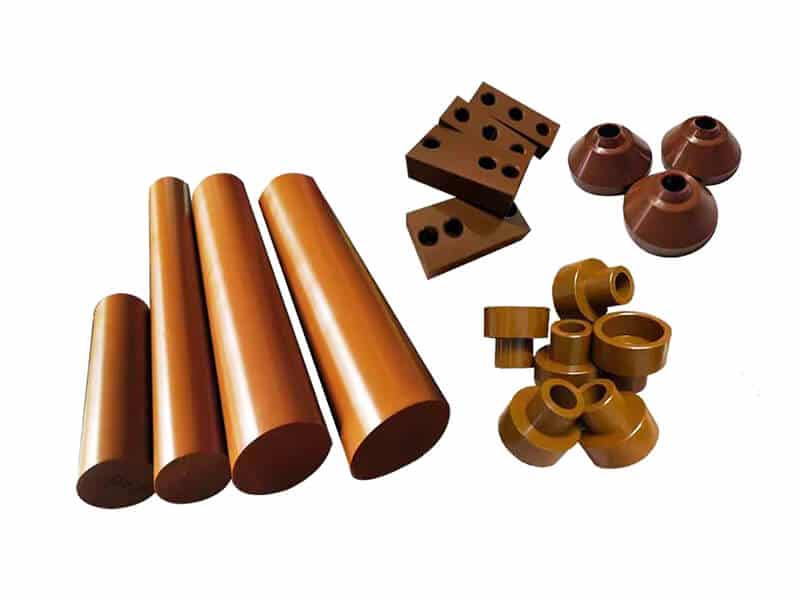
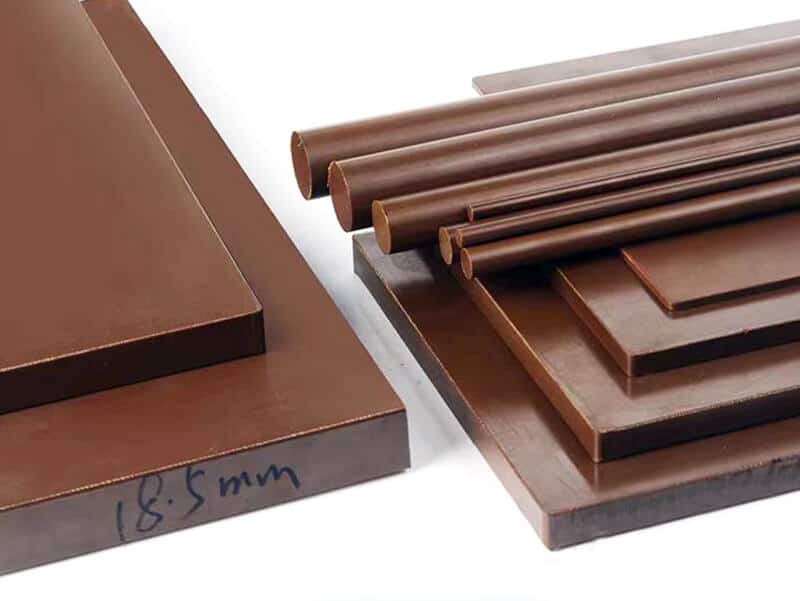
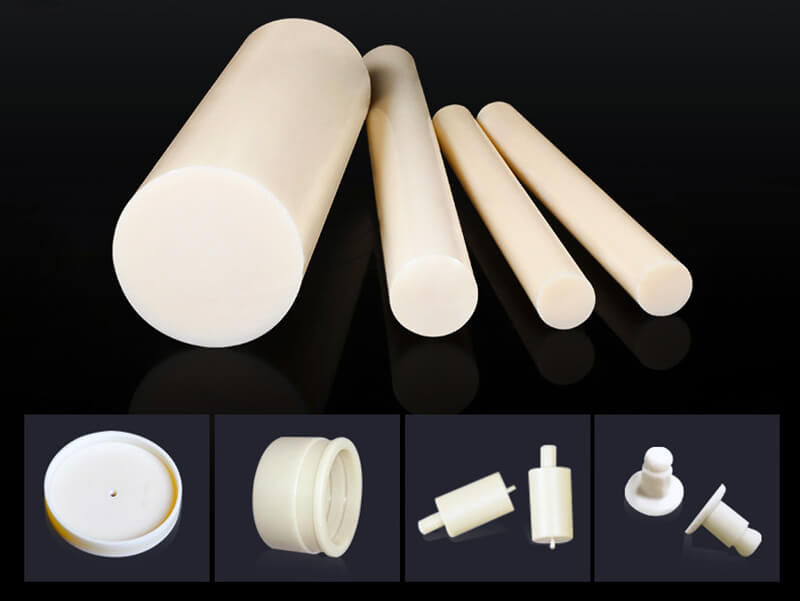
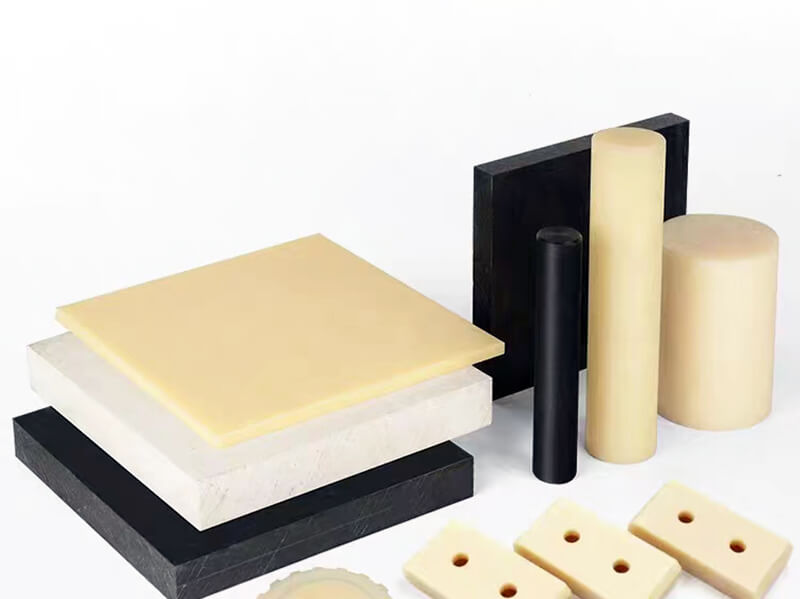
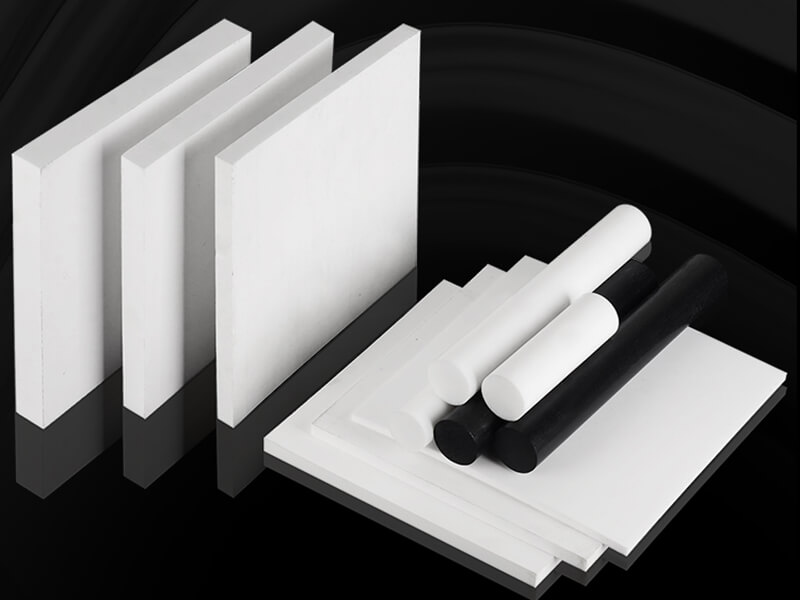
About pVDF Plastic
PVDF, full name polyvinylidene fluoride or polyvinylidene difluoride, is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer produced by the polymerization of vinylidene fluoride. Its density is 1.78 g/cm3, and the natural color is white.
Compared with PTFE, PVDF offers higher impact resistance and rigidity at temperatures up to 150℃. PVDF also provides excellent chemical resistance, abrasion resistance, flame resistance, and UV stability.
PVDF material is commonly used in the chemical, semiconductor, medical, and defense industries, as well as in lithium-ion batteries.
pVDF Plastic That UVTECO Supply
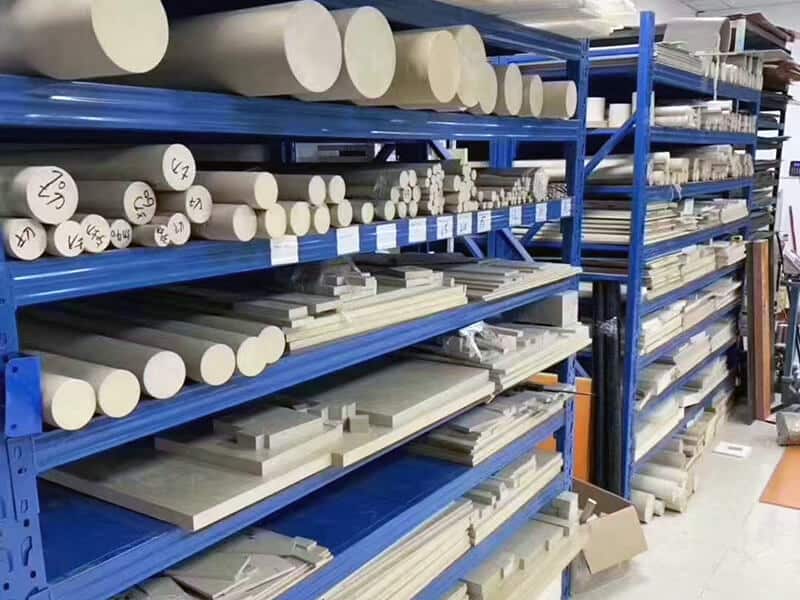
Profile/Shape
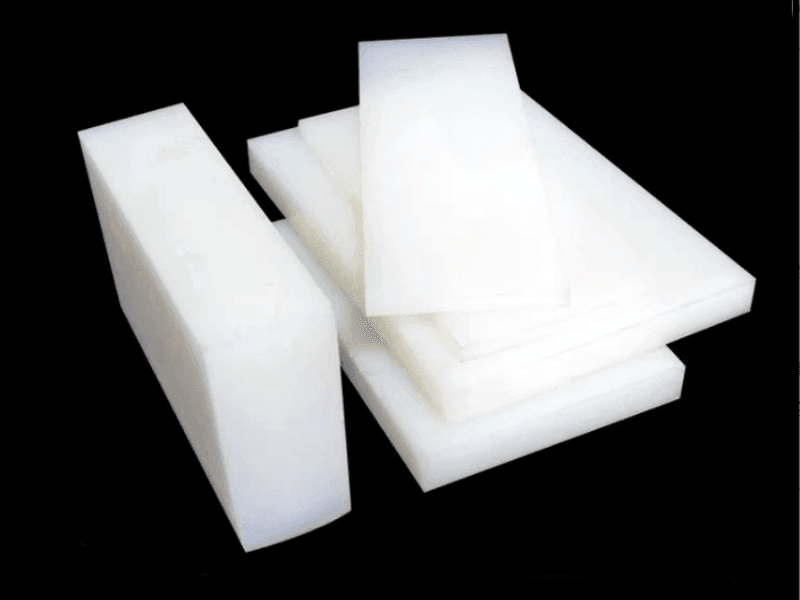
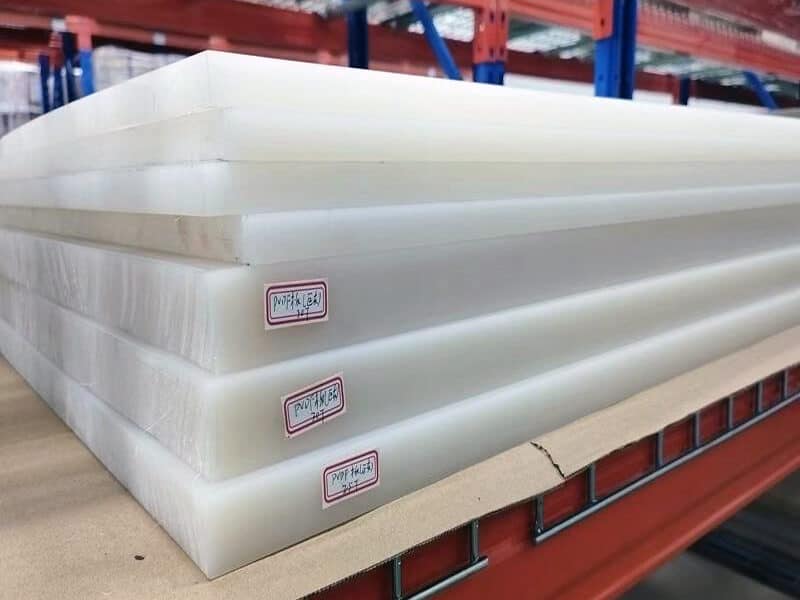
- Sheet
- Film
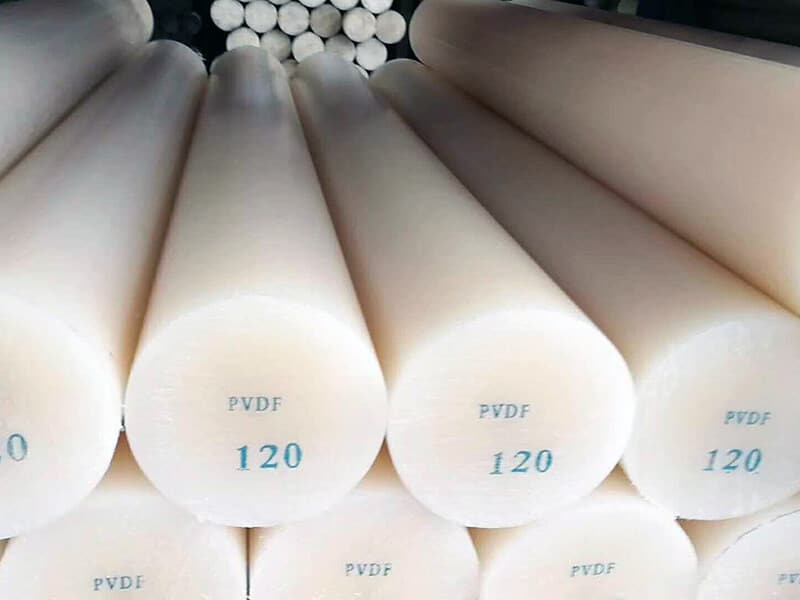
- Rod
- Tube
- PVDF Welding Rod
Grade
- Virgin
Color
- Nature (white)
- Transparent (PVDF Film)
- Red (PVDF Film)
Production process
- Extrusion
- Mould Pressing
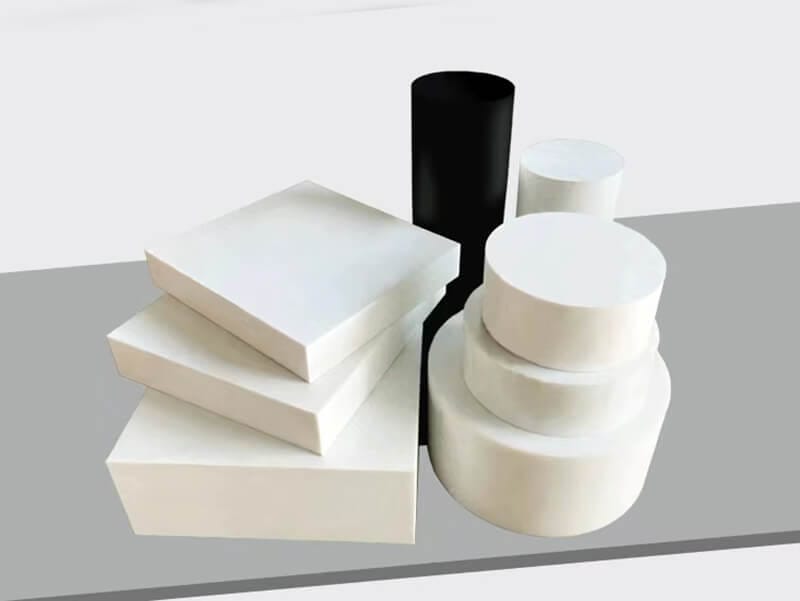
PVDF Sheet
- Thickness: 2 to 100mm
- Width: 510 to 1500mm
PVDF Film
- Thickness: 25μm, 30μm, 50μm
- Length: 1500m/roll
PVDF Rod
- Diameter: 10 to 300mm
- Length: 1000mm or Custom
PVDF Tube
- Diameter: 16 to 315mm
- Thickness: 1.5 to 9.6mm
- Length: 5000 mm
PVDF Welding Rod
- Diameter: 3mm, 4mm, 5mm
- Length: 540 m/roll, 300 m/roll, 195 m/roll
Remark
- All sizes can be customized according to the requirements of clients;
- Machining services are available;
Properties of PVDF Material
| Basic Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Material Name | PVDF, Polyvinylidene Fluoride, Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| Density | 1.78 g/cm3 |
| Natural Color | White |
| Processing technology | Extrusion, Mould Pressing, Injection Molding |
| physical properties | testing standard | unit | value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | ISO 1183-1 | G/cm3 | 1.78 |
| water absorption (immersion 24 hours) | iSO 62 | % | <0.1 |
| Mechanical Properties | Testing Standard | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | iSO 527 | Mpa | 55 |
| Tensile Modulus of Elasticity | iSO 527 | Mpa | 2200 |
| Tensile strain at yield | iSO 527 | % | 9 |
| Tensile strain at break | iSO 527 | % | 30 |
| Charpy impact strength (unnotched) | iSO 179 | KJ/m2 | no break |
| Charpy impact strength (notched) | iSO 179 | KJ/m2 | 10 |
| Ball indentation hardness | ISO 2039 | n/mM2 | 110 |
| Rockwell Hardness | ISO 2039 | m78 |
| thermal properties | testing standard | unit | value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting temperature (DSC, 10 °C/min) | ISO 11357 | ℃ | 175 |
| Temperature of deflection under load (1.8 mpa) | ISO 75 | ℃ | 105 |
| coefficient of linear thermal expansion | – | M/(M.K) | 190X10-6 |
| min service temperature | – | ℃ | -50 |
| max continuous service temperature in air | – | ℃ | 150 |
| thermal properties | testing standard | value |
|---|---|---|
| Flammability | UL94 | v0 |
| thermal properties | testing standard | unit | value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric strength | IEC 60243 1 | kV/mM | 18 |
| Electric strength | IEC 60093 | OHM.cM | >1014 |
| Surface resistivity | ANSI/ESD STM 11.11 | OHM.SQ | >1013 |
Main Usage of PVDF Material
- Pipelines
- Filter plates
- Pump and valve parts
- Fittings, seals, and gaskets
- Electrical and Electronic Devices
- Chemical Processing Equipment
- Fluid handling components for petrochemical industry
Main Feature of PVDF Material
- High abrasion resistance
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Extremely low moisture absorption
- Good welding property
- Excellent inherent flame resistance
- Good dimensional stability
- Good electrical insulation
- Good UV & weather resistance
- High operating temperature
- Ourstandaing Machinability
Can’t find what you need? Or need a custom pVDF Plastic?
Leading supplier of PVDF Material and machining service
UVTECO has begun to be active in PVDF Material since 2013, we know more PVDF Material, including raw materials, additives, production processes, machining solutions, etc. With our rich experience in this field, we have become a leading supplier of PVDF Materials, including sheets, rods, tubes, welding rods, custom extruded profiles, etc.
We stock frequently used PVDF sheets, PVDF rods, PVDF tubes, PVDF Film, and PVDF welding rods for fast delivery to global clients. Otherwise, we provide machining services. Today, UVTECO provides high-quality PVDF parts/components for over 2,500 clients from more than 45 countries. They are active in chemical processing, semiconductor, electroplate, water treatment, solar energy, oil and gas, etc,
Contact UVTECO for machining UHMW Plastic
NEED HELP FROM ENGINEER FOR PLASTIC PARTS
If you need to submit files, please send email to info@uvteco.com
Related Blogs about pVDF Plastic
Process of Machining Nylon
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticWhat is G10 Epoxy Sheet
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticG10 Vs FR-4
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticFR-4 Printed Circuit Board
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticCNC Machining FR4 and G10
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticNylon 101
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticDigital Printing On Acrylic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPlastic Sheet for Skylight
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPolypropylene Vs Acrylic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPlastic Forming Process
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticMachining Polyimide Plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPETG Vs. Acrylic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticABS Plastic Property
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPainting Plastic Car Parts
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticHow to Polish Polycarbonate
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPET injection molding
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticNitrocellulose Vs PVDF
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPlastic for Signage
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticWhat is PEEK plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticAcrylic Vs Polycarbonate
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticDifference HDPE Vs PET
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticDifference PVDF Vs PTFE
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticPEEK Bushing and Bearing
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticHow to Machine PEEK Plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticFood Grade Plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticDifference ABS Vs HDPE
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticABS plastic Application
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticABS Vs PVC
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticMachining UHMW Plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticAcetal Vs Polypropylene
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticHDPE Vs Acrylic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticHDPE Vs PVC plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticHDPE Vs ABS
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticHDPE vs UHMW
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticTeflon vs UHMW
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticDelrin vs UHMW
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticAcetal Vs. UHMW plastic
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About PlasticWhat is Rapid Tooling?
By UVTECOPosted in Blogs About Plastic
Frequently Asked Questions about pVDF Plastic
PVDF is a special kind of engineering thermoplastic. It is one of the world’s toughest and purest materials, and it is used in different industries. The material is often known by its trade name Kynar®.
It is rigid, abrasion-resistant, and flame-resistant, ensuring robust performance in various applications. This high-grade material is opal or milky in color, meaning it features a cloudy or white appearance, like the inside of a seashell.
No! PVDF and Teflon are two different types of polymer materials. The raw material of PVDF is polyvinylidene fluoride, and the raw material of Teflon is PTFE. Both materials differ in chemical structures, physical properties, and applications. Typically, Teflon has a higher temperature resistance, up to 260℃. PVDF’s temperature resistance ranges from 150 to 175℃
PVDF and PVC are different polymer materials with distinct chemical and physical properties. The density of PVDF is 1.78 g/cm³, whereas the density of PVC is about 1.4 g/cm³. PVDF operates at higher temperatures, up to 284°F, while PVC starts deforming at around 140°F. PVDF is much stronger compared to PVC and ensures robust performance in various applications.
PVDF is manufactured from heavier gauge metal panels and high-quality paint, which increases its longevity. The material is also used in high-demand applications like the automotive, aerospace, defense, battery, and electrical industries. Its high-grade raw materials, superior physical and chemical properties, and reliable performance in such applications make it an expensive polymer material compared to others.
PVDF is a naturally hydrophobic material that is highly resistant to water. It can handle all kinds of weather conditions without deforming or getting damaged. Whether it is hot, cold, rainy, or sunny, the coating applied ensures safety. Its hydrophobic properties make it corrosion-resistant and durable. This is why it is one of the most reliable choices for various waterproof and breathable applications.
PTFE and PVDF are both high-grade polymer materials with some similar properties. However, both materials feature different chemical and physical properties. Typically, PVDF offers better mechanical stability than PTFE, which makes it suitable for use as an effective filtration in various non-aggressive aqueous and mild organic solutions.
Yes, of course. PVDF is an acid-resistant polymer because of its excellent chemical and mechanical properties. Its exceptional mechanical stability prevents it from changing or breaking down easily when exposed to harsh chemicals. The material is particularly resistant to inorganic and organic acids. It also effectively handles hydrocarbons and halogenated solvents, which is why it is widely used in industries that deal with chemicals.
PVDF is one of the capable binders for the cathode in lithium-ion batteries. It effectively keeps the electrodes in batteries stable and prevents them from breaking down. Even when the battery gets hot or is charged many times, the material maintains its structural stability and ensures the best performance.
PVDF sheet is a special kind of sheet made from a high-performance thermoplastic polymer. It features outstanding durability, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Besides, it has excellent UV, corrosion, and radiation resistance that can be easily used in food-contact applications and other various industrial materials. The sheet typically tends to be tough and durable, lasting a long time even in harsh conditions.
In chemical processing applications, PVDF is used in various forms like pipes, tanks, pumps, and valves. It has excellent corrosion, thermal, physical, and chemical resistance, which helps to maintain its stability in all conditions. Due to these excellent properties, the PVDF does not get damaged while in operation and helps keep things like tanks, pipes, or containers safe.
Yes, PVDF is a high-quality machinable material that performs the same as other metals. Its dimensional stability and robust toughness don’t break down its structure while in the machining process. Even by following the right steps in machining, PVDF produces high-precision components that are used in many industrial applications, like piping, tubing, valves, tanks, nozzles, and fittings.
Yes, PVDF can effectively be welded. Some of the common welding methods for this high-quality material include heat contact, hot gas welding, ultrasonic, hot lamination, infrared, electrofusion, resistance heating, spin, and radio frequency welding. PVDF is a very rigid and hard plastic that doesn’t bend easily in the welding process. In most cases, it must be melted at a high temperature and then used to join two pieces of material in welding.
PVDF can be joined in different ways. Contact welding, radiant heat, and RF induction are some effective processes for joining PVDF. In the welding process, methods such as spark fusion, butt fusion, beadless fusion, and infrared methods are commonly used. However, it is important to clean and shape the pipe ends carefully and remove any weak outer layers before welding.
No, PVDF is non-flammable. It won’t burn or ignite when exposed to flames or high heat. PVDF’s LOI of 44% means it requires a high oxygen concentration to ignite. Rather than that, it is self-extinguishing and has good resistance to UV light. This makes the polymer a reliable choice to use in environments where fire could be a risk.
Yes, PVDF is recyclable but requires special processes to catch the components due to its chemical stability. Typically, it is recycled through solvent extraction, where a special liquid is used to separate different materials. The process starts by soaking broken diaphragms in this organic solvent, which breaks down the PVDF in a way that can be reused. The leftover material is called sediment, which is a type of fabric known as nonwoven and can also be recovered.
PVDF resin is considered safe and biocompatible. Thus, it can effectively be used in the food industry and various biocompatible devices like hernia meshes or internal devices. Due to its non-toxicity, it is widely used in water treatment systems around the world to help ensure clean water.

Looking for a trustworthy Supplier
Need a Trustworthy Supplier of Plastic, Foam, Sponge, Rubber, Metal, and Machining Solution. Click the Button, We Will Be In Touch With You As Quickly As Possible.