Nylon (PA6, PA66) plastic in all forms
Nylon 6, Nylon 66, Cast Nylon, Extruded Nylon, Nylon Sheet, Nylon Rod, Nylon Tube, Machining Nylon Parts…About Nylon Plastic
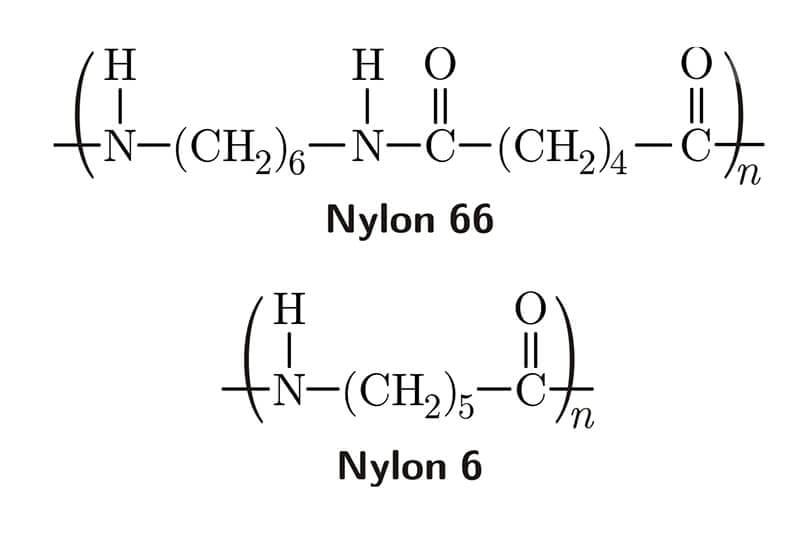
Nylon plastic is a common thermoplastic engineering material, which was developed by DuPont company in 1938, and its density is 1.15 g/cm3. Normally, it is frequently used as a replacement for bronze, brass, aluminum, steel, and other metals, as well as other plastics, wood, and rubber. Some people call it different names, for example, Polyamide, PA, PA6, PA66, Nylon 6, Nylon 66, Cast Nylon, etc. Nylon plastics are classified according to numbers (6, 66, 11, 12, 46, etc.), which means molecular structures. The common types are PA 6, PA 66, PA 610, PA 46, PA 69, PA 612, PA 11, and PA 12.
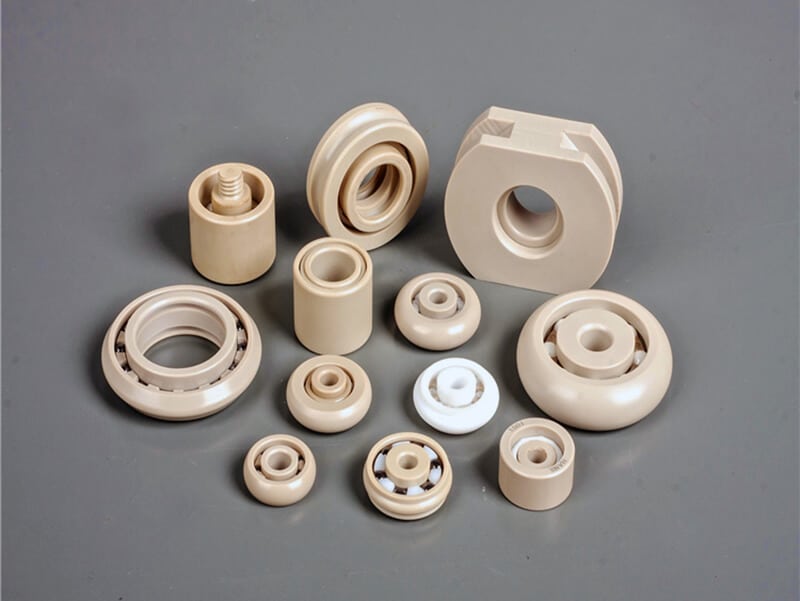
Nylon plastic has better tensile strength and bending stiffness than Acetal plastic (Polyoxymethylene POM) but offers a poor Water Absorption Rating. Nylon plastic offers excellent impact resistance, lightweight, good stiffness, low frictional properties, and outstanding wear properties. It also has very good temperature, chemical, and impact resistance properties. Normally, Nylon is frequently used to replace metal bearings and bushings often eliminating the need for external lubrication. Other benefits include reduced part weight, less operating noise, and decreased wear on mating parts.
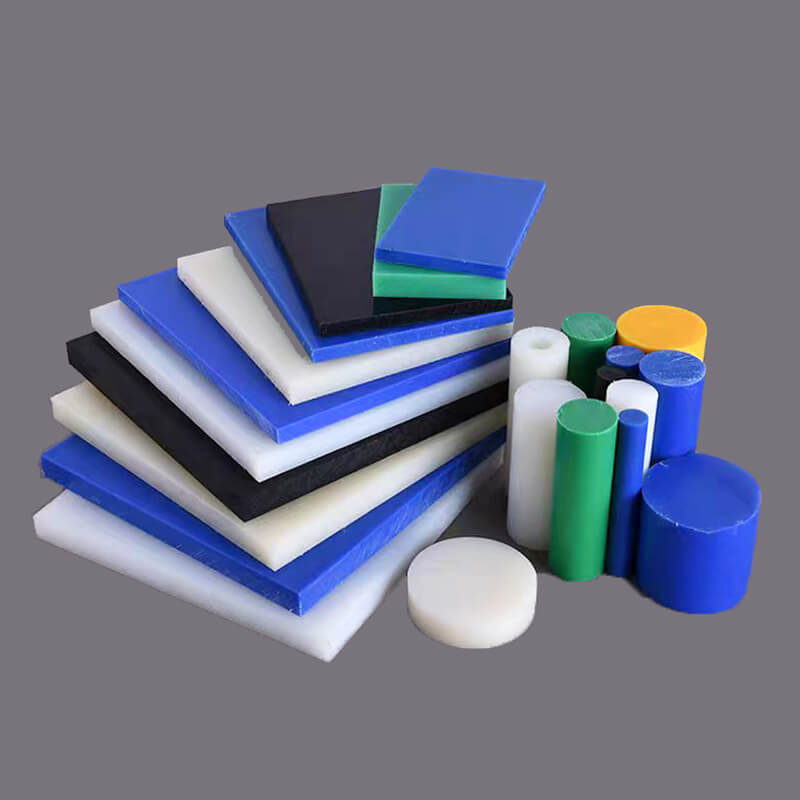
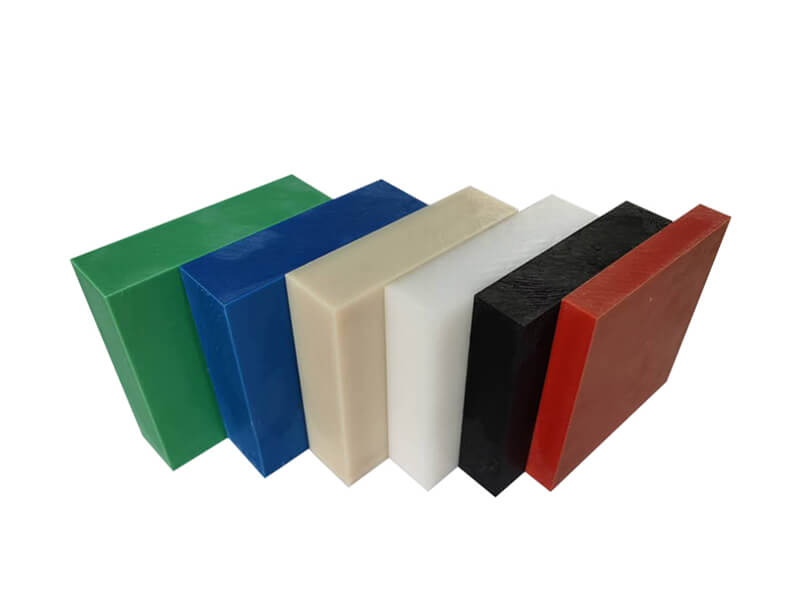
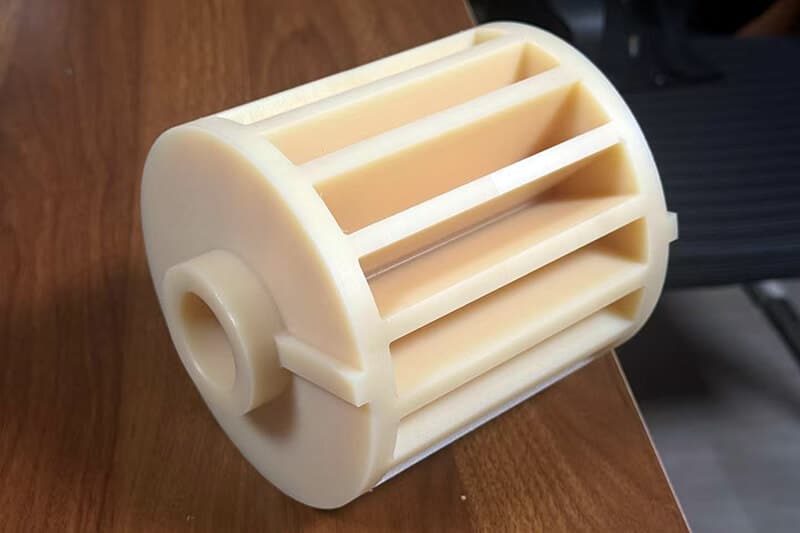
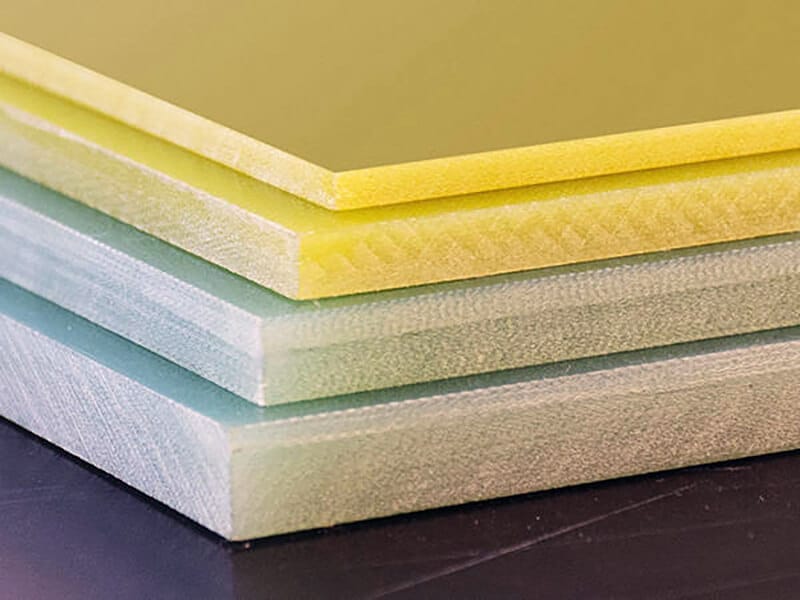
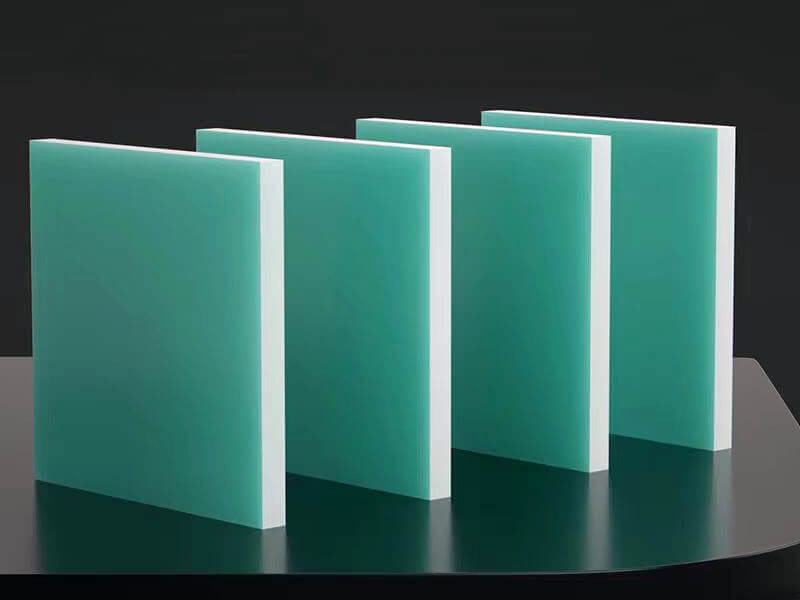
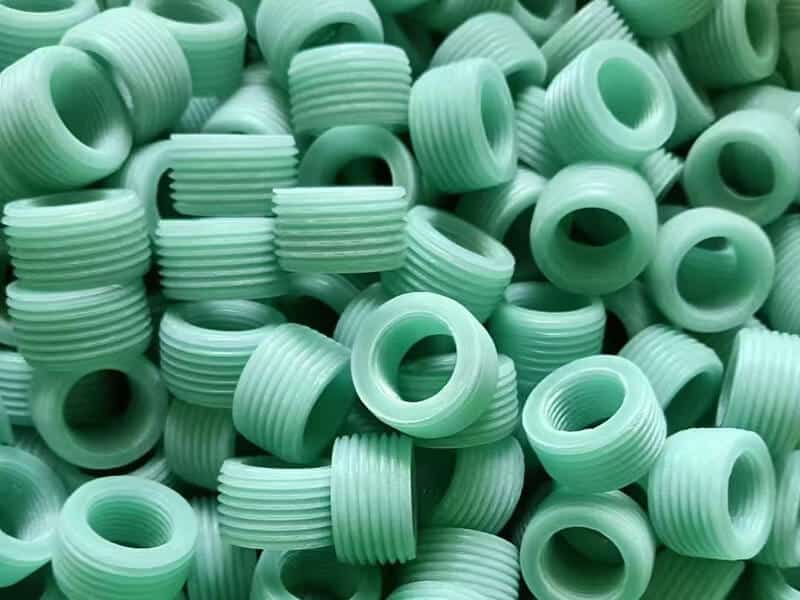
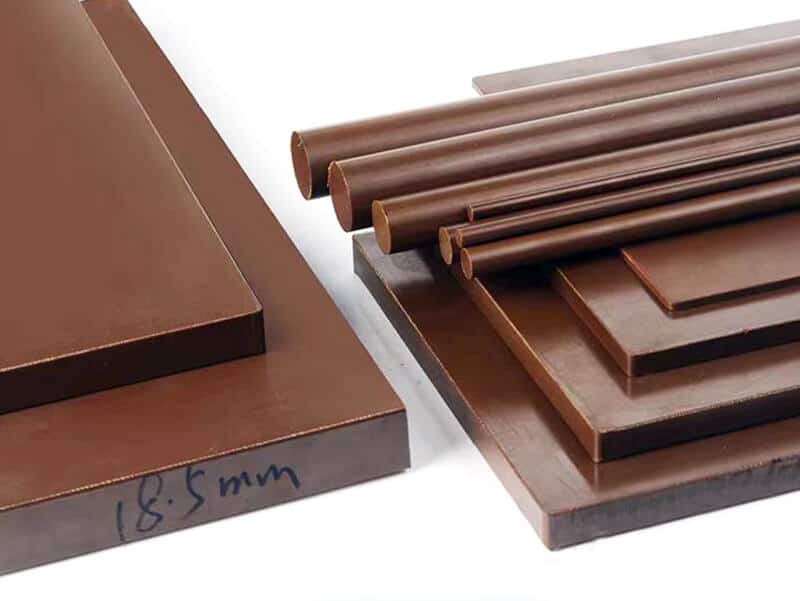
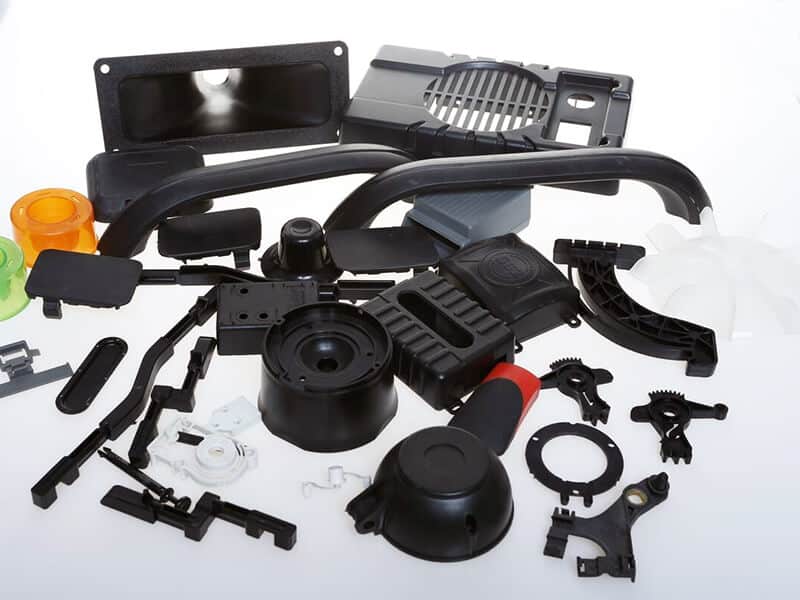
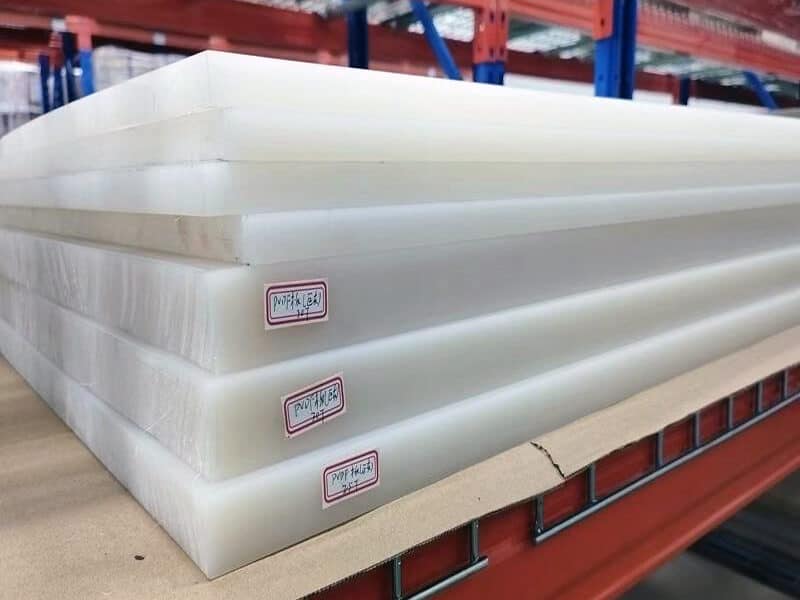
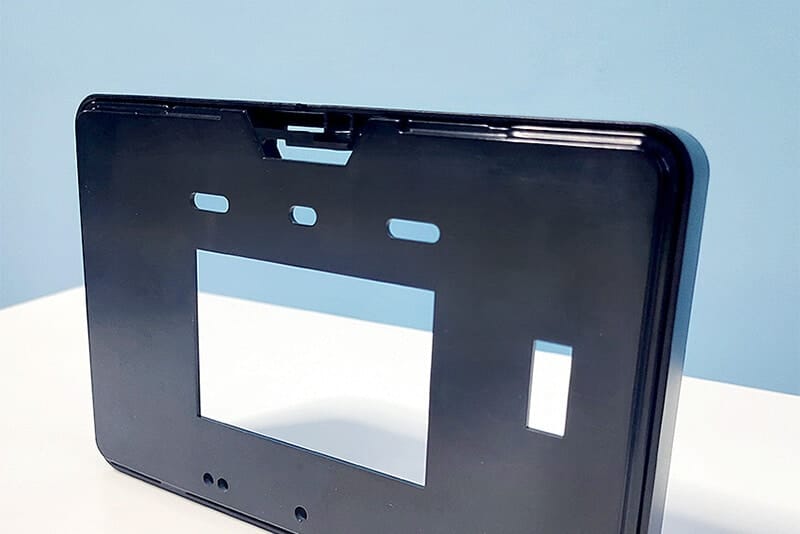
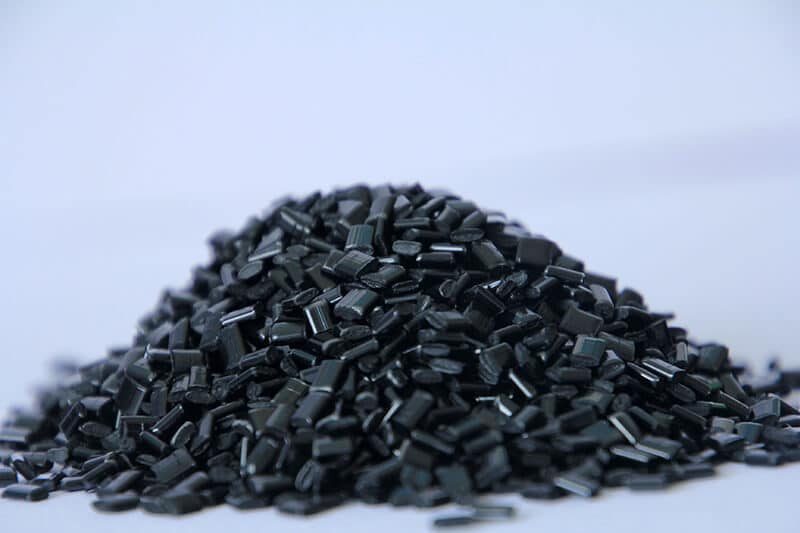
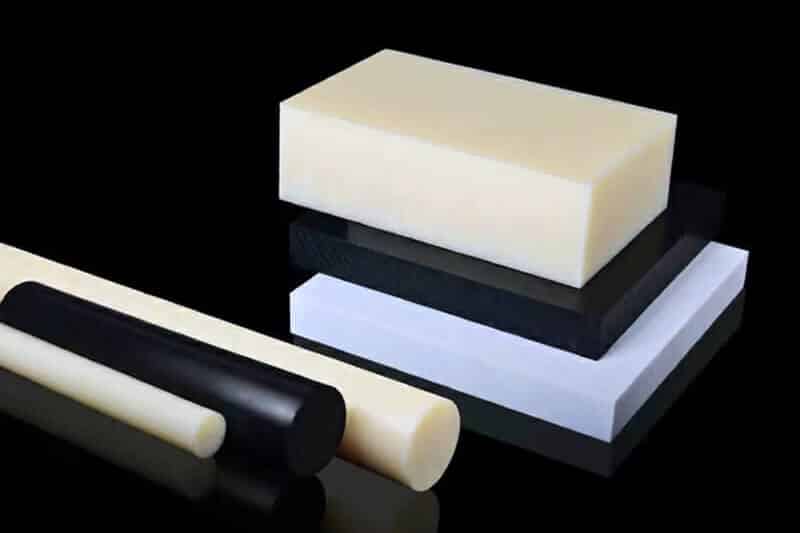
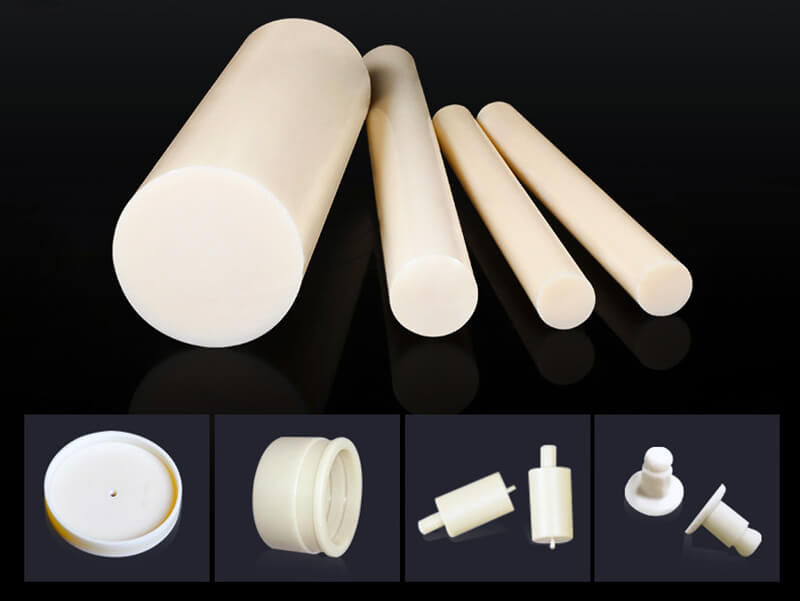
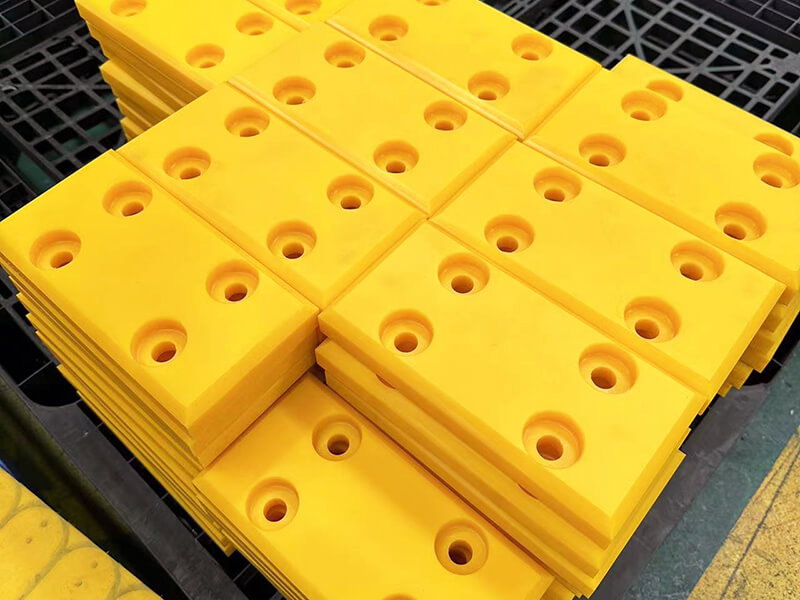
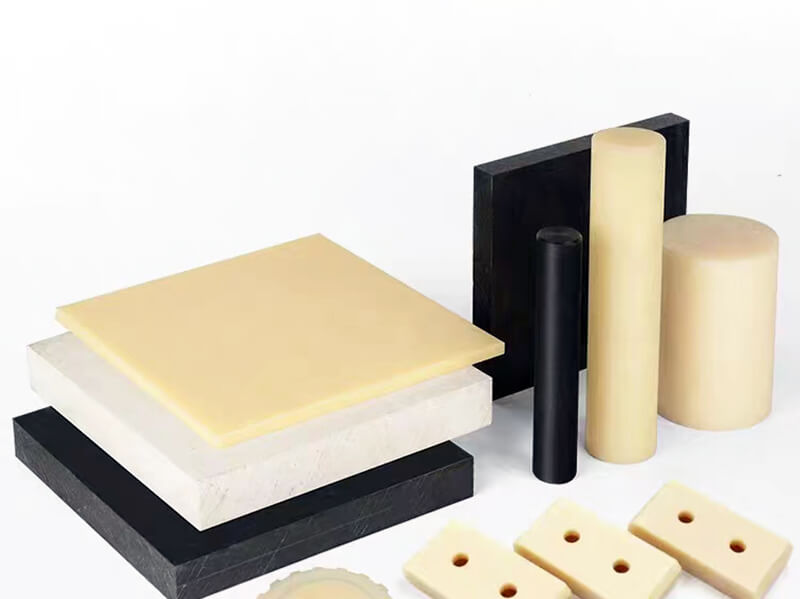
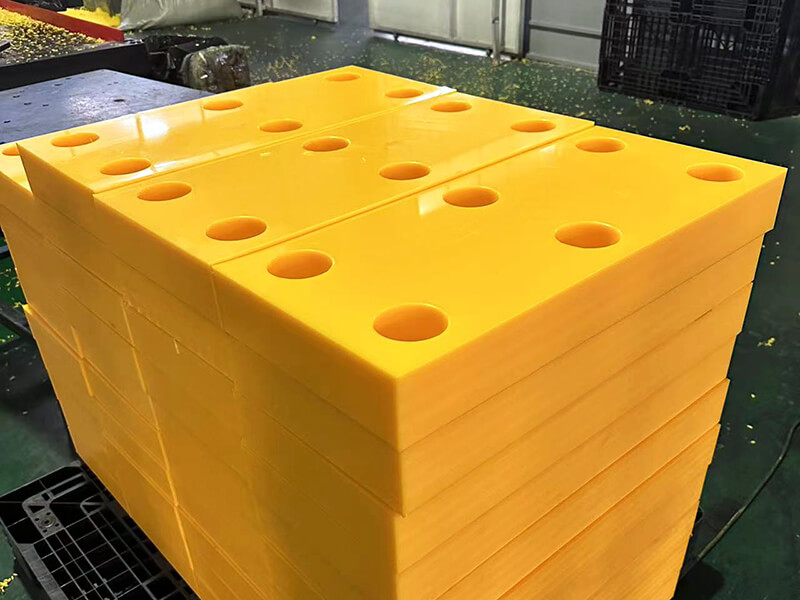
The standard stock shapes of Nylon are sheet, rod, and tube, which are produced by the cast molding and extrusion processes. The main materials are Nylon 6 (PA6) and Nylon 66 (PA66). Then, you can use a cutting machine or CNC machine to machine them into parts. The natural color of the Nylon Sheet/Rod/Tube is off-white. In addition, you can find Black, Green, Blue, Red, etc. Injection molding is another process that involves large quantities of nylon parts. 3D printing is a popular process for low-quantity Nylon parts.
Some manufacturers can get the enhanced Cast Nylon Sheets in some physical properties by adding different additives, such as Glass Fibers, Oil, Solid Lubricant, MoS2 (Molybdenum Disulfide), Elastomer, etc. They are called Unfilled Nylon, Glass-filled Nylon, Oil-filled Nylon, MoS2-filled Nylon, and Moly-filled Nylon.
Specification of Nylon (PA) Plastic Product
Profile/Shape
Grade
Modified Nylon (PA)
Color
Nylon Sheet/Block
Nylon Rod
Nylon Tube
Custom Profile
Remark
Properties of Nylon Plastic
Main Usage of Nylon Plastic
Main Feature of Nylon Plastic
Industry
Can’t find what you need? Or have a technical question?
Leading Supplier of Nylon (PA) Plastic in China
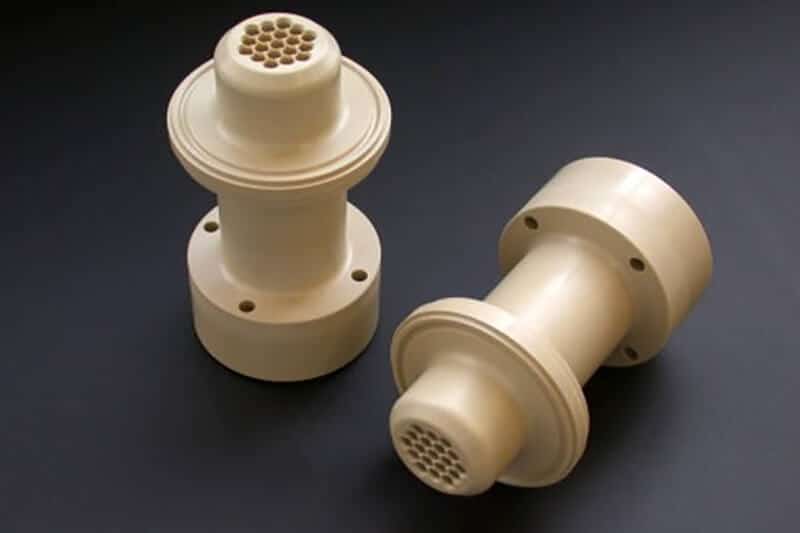
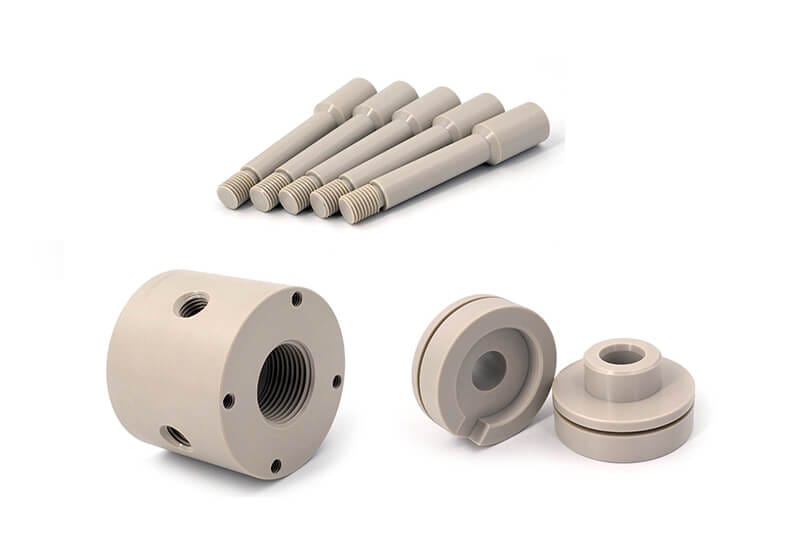
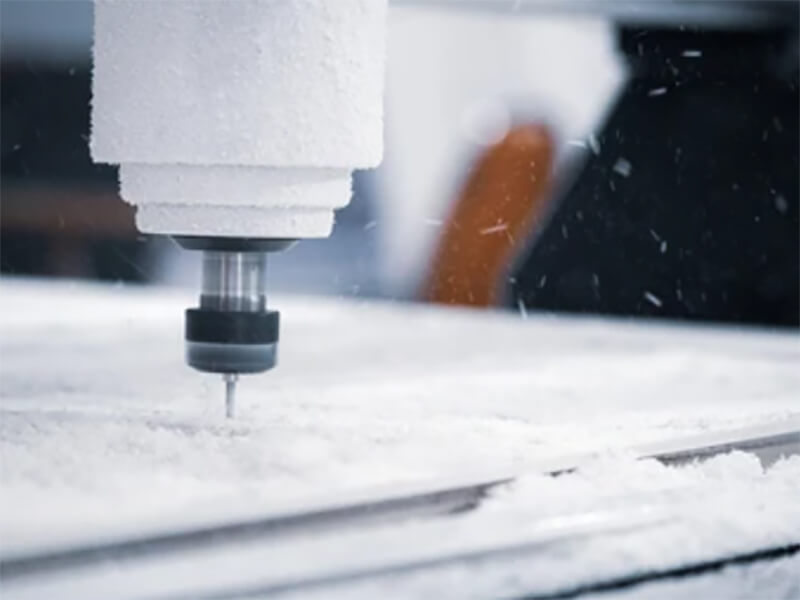
UVTECO was involved in Nylon (PA) Plastic in 2003. With cooperation with top suppliers of Lucite around the world, UVTECO can manufacture high-quality Nylon Sheets, Rods, and Tubes. Meanwhile, UVTECO provides an integrated machining solution for Nylon-based parts/components; the main machining methods include cutting to size, drilling, 3-axis and 5-axis CNC milling, CNC Turning, injection molding, thermal forming, engraving, etc.
UVTECO stores Nylon sheets/blocks/rods/tubes in frequently used sizes for fast delivery. As an ISO-certified company, UVTECO provides high-quality nylon-based products and parts/components for over 2,500 clients from more than 45 countries.
Contact UVTECO for machining Nylon service
Related Blogs about Nylon Plastic
Frequently Asked Questions about Nylon

Looking for a trustworthy Supplier
Need a Trustworthy Supplier of Plastic, Foam, Sponge, Rubber, Metal, and Machining Solution. Click the Button, We Will Be In Touch With You As Quickly As Possible.