A Guide to Popular Plastic Forming Process
Dive into the world of plastic forming processes. Learn about molding, extrusion, and more in this comprehensive guide.

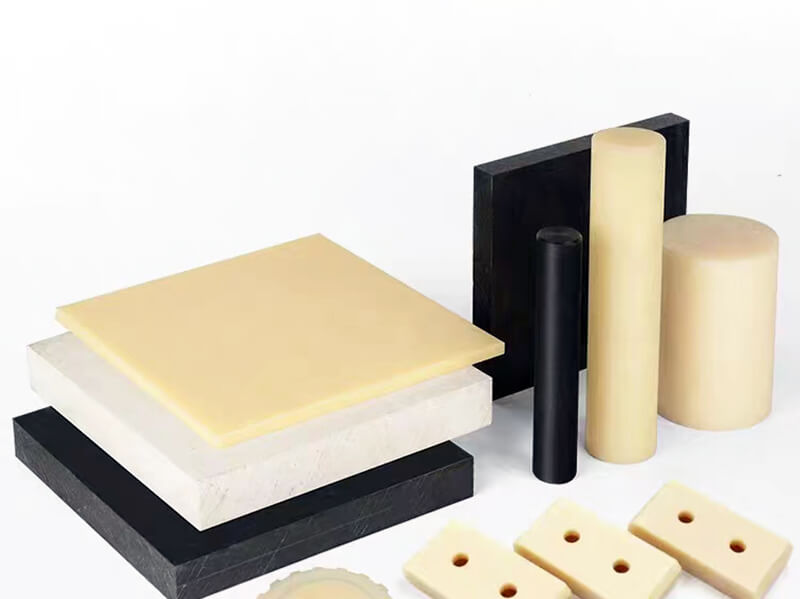
It is undeniable that activities in modern life are significantly dependent on plastic material. These materials, plastics, are now an integral part of almost every application. However, depending on the using criteria, there are several types of plastics that have been developed throughout time. And based on different applications, desired characteristics of the final product, used material type, etc., the forming processes of all plastics are not the same.
There are various common plastic forming processes available, like molding, extrusion, thermoforming, and so on. The choice of a particular process profoundly impacts the end product’s quality, efficiency, and sustainability. For any designer or engineer engaged in product development, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of these manufacturing processes to incorporate the emerging advancements in the future methods of producing components.
Here, we elaborate on the different forming processes of plastics, including methodologies, strengths, weaknesses, etc.
In-depth Discussion on Common Plastic Forming Processes
Common plastic-forming processes are the key terms of modern manufacturing industries of various sectors. In this in-depth discussion, we provide detailed information on the prominent procedures for forming the most useful and common plastics.
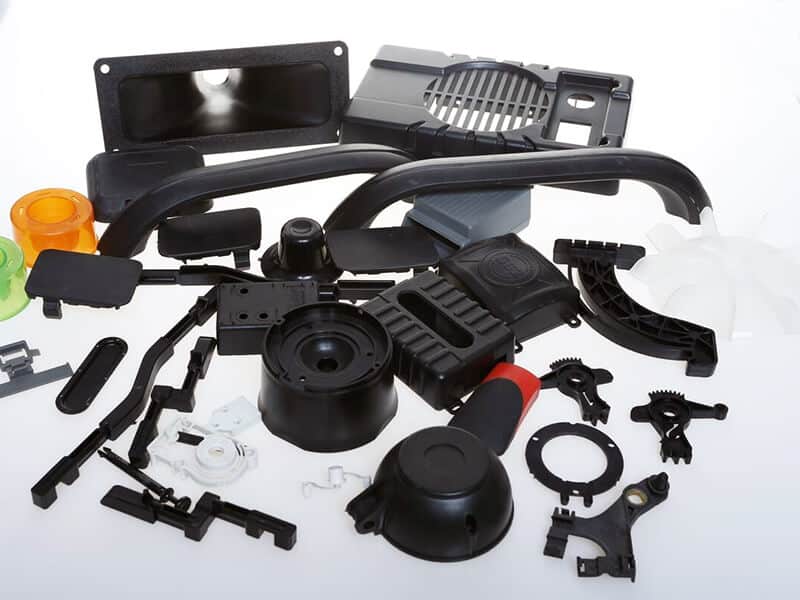
Plastic Injection Modling
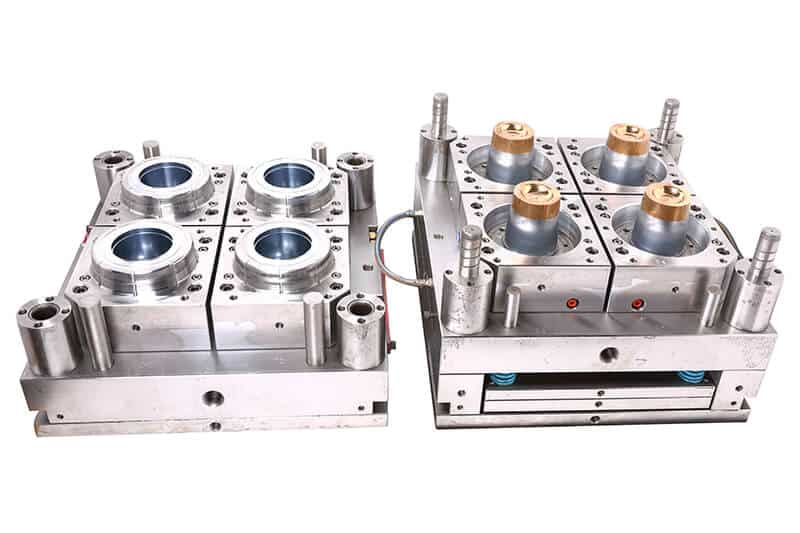
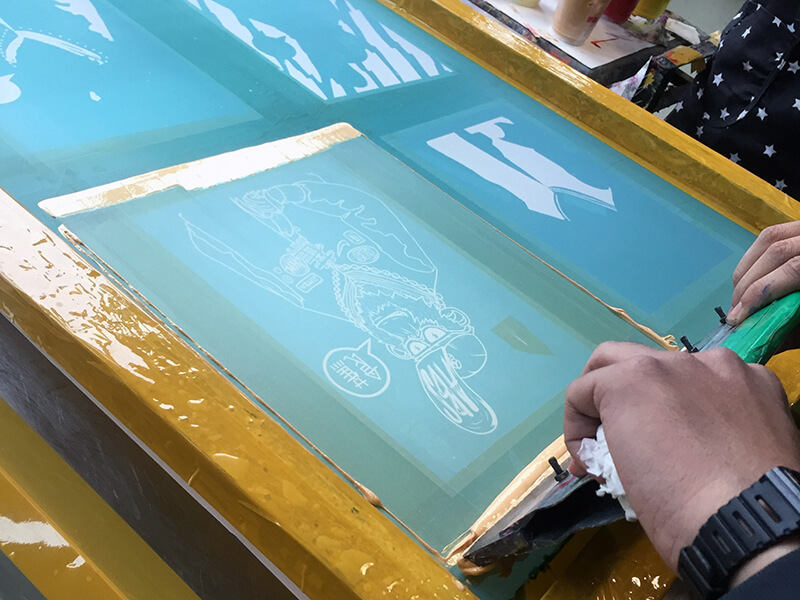
Injection molding was invented by American inventor John Wesley Hyatt and his brother, Isaac, in 1872. Injection molding is considered a swift and high-precision procedure for creating diverse plastic products. It involves heating chosen plastic granules and injecting them into precisely crafted molds.
Here, the shaping used to be decided earlier to get the perfect shaped items. Injection molding’s versatility shines in applications like packaging, automotive components, toys, and medical items. It must be mentioned that the Second World War played a pivotal role in boosting injection molding due to the demand for mass-produced plastic products in a cost-effective way.
Rotational (Roto) Molding
The process of rotational molding, also known as roto-molding, involves filling a hollow mold with powdered plastic resin, and then initiating a biaxial rotation under controlled heat. In the rotational process, the resin slowly melts and gradually sticks to the mold’s inner walls.
Finally, the desired shape of plastic is formed. Here, cooling the heated plastic item is essential to ensure adequate hardness. However, this process’s success depends on factors like ambient conditions, mold type, material specifications, and powder quality. One must mention that Roto molding is favored for crafting hollow items at a very low price
Extrusion Blow Molding
This particular process is a two-step procedure used to craft plastic objects. It starts by generating a hollow tube, named parison, and made from molten plastic. Following this, the parison is inflated into the desired shape within a mold. As the parison grows bigger, it takes on the shape of the mold and stays that way when it cools down. However, there are generally two particular ways to perform extrusion blow molding:
3D Printing
There are two main plastic processing procedures in 3D printing. The first is FDM, which uses three procedures to process plastic: sintering with powders (powder bed fusion), photopolymerization using liquid polymers, and material extrusion. The second process is subtractive manufacturing, which creates components by removing material.
Here, unwanted material is removed from a solid blank through grinding, drilling, or milling to create a smaller plastic component. However, parts produced through 3D printing require post-processing in both processes to achieve improved dimensional and desired finishing accuracy.
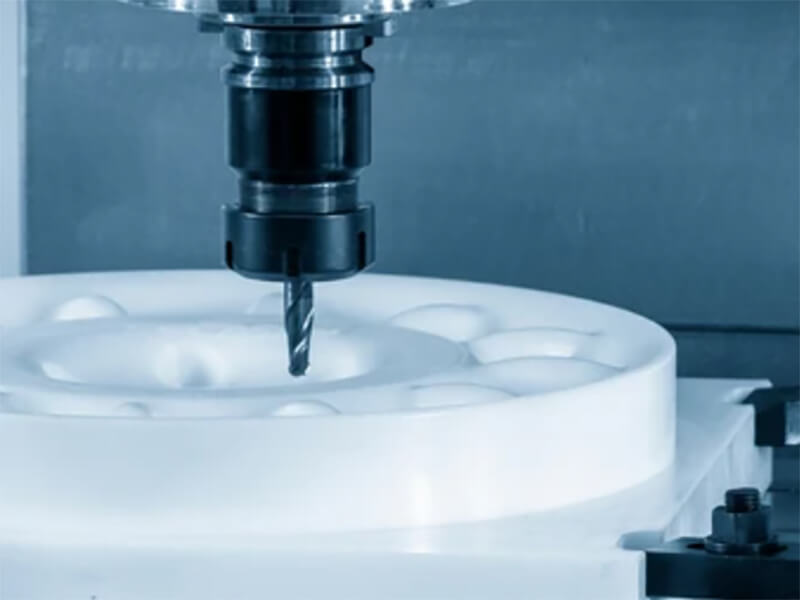
CNC Machining
CNC machining of plastics is a bit more complex than others. This process is used for turning, cutting, drilling, providing complex designs, etc. Plastic CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process. Here, in general, a solid plastic block is positioned against a moving cutting tool, which gradually removes material from the block to generate the desired shape or design.
The machine’s speed, movement, feed rate, etc., are predetermined by guided computer-based software like CAD. Advanced technology integrated into CNC machines enables the creation of intricate shapes and fine details. The typical process unfolds in three stages: initiating with computer-aided design, followed by the actual machining of the design, and concluding with the finished part. It is considered the most modern and advanced approach to plastic processing.
Polymer Casting
In our opinion, it is the simplest process of plastic formation. In this formation technique, liquid polymer is poured into a mold in the form of resin or rubber. Then, time is allowed for natural solidifying.
We must mention that some additional post-processing actions are required after casting as this process imposes a limitation on the used mold after a single use due to its chemical characteristics. However, it is the most lucrative plastic forming process for artists who create plastic sculptures and intricate volumetric components.
Injection Blow Molding
Injection blow molding is a distinct approach from traditional extrusion. Instead of a parison, the precursor is called a “preform.” This method integrates an injection unit within the machine and employs a multi-impression mold assembly. Here, the mold cores are mounted on a rotary table. These cores do two jobs: they act as blowing pins and rotate 120 degrees between injecting, blowing, and ejecting stations.
To differentiate this process from others, injection blow molding is a manufacturing technique specifically tailored for crafting hollow plastic items like bottles and containers. The process initiates with the melting of thermoplastic materials like PE, PP, or PET. Then, within an injection molding machine.
After that, the molten plastic is injected into a preform mold, shaping it into a tube-like structure called a preform. Finally, it is clamped into a mold cavity and sealed. Injection blow molding is renowned for delivering high-quality items characterized by impeccable surface finishes and precise dimensions. Lastly, this technique is usually utilized to produce plastic containers for the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
Reaction Injection Molding (RIM)
RIM is a contemporary method. It is used to produce robust structural foam from plastic. In this plastic-forming process, highly reactive plastic liquids are combined under significant pressure and placed into a mold. Here, these liquids react and polymerize inside the mold and form lightweight foamed plastics.
Vacuum Casting
Vacuum casting is a comparatively economical solution in plastic forming processing. Professionals highly favor it as it provides great output by producing a limited quantity of top-quality rapid prototypes. There is no need for specialized tools, so the budget is saved on substantial investments in tools or materials.
In the process, a master model is used to generate a 3D-printed master pattern, which is positioned within a sealed enclosure. Following this, that enclosure is filled with a flexible urethane or silicone material. When the 3D master is removed, it leaves behind a cavity within the mold, ready to be filled with plastic resin to create a replica of the original. Finally, vacuum pressure is imposed to ensure it fills completely without any unwanted air bubbles.
Thermoforming
This plastic forming process is designed to shape plastic sheets into 3D forms using heat, vacuum, and pressure, primarily thermoplastics. It is commonly used for items like cups, lids, packaging, and auto parts made from suitable plastics that become pliable when heated and rigid as they cool.
Compression Molding
Compression molding is another shaping technique where plastic material is directly inserted into a heated metal mold. The heat softens the plastic. And it causes the softened plastic to adapt to the mold’s shape as it closes. After molding, any surplus flash may be trimmed away.
How to Choose the Right Plastic Manufacturing Process?
Well, now we already know several processes are available to form plastic. But how to choose the right one? Here, we solve this burning question by considering four factors.
How to Choose a trustworthy supplier of Plastic Molding parts?
Firstly, a trustworthy supplier of plastic parts should know the different properties of plastic, including mechanical, optical, physical, electrical, and thermal properties.
Then, a trustworthy supplier of plastic parts should have a lot of history projects in the Plastic Forming Process for different industries.
As a leading supplier of plastic material in China, UVTECO knows all properties about different plastic material. And have a lot of projects of molding plastic parts. If you are looking for a trustworthy supplier of Plastic parts, contact us now!
Related Blogs

Looking for a trustworthy Supplier
Need a Trustworthy Supplier of Plastic, Foam, Sponge, Rubber, Metal, and Machining Solution. Click the Button, We Will Be In Touch With You As Quickly As Possible.