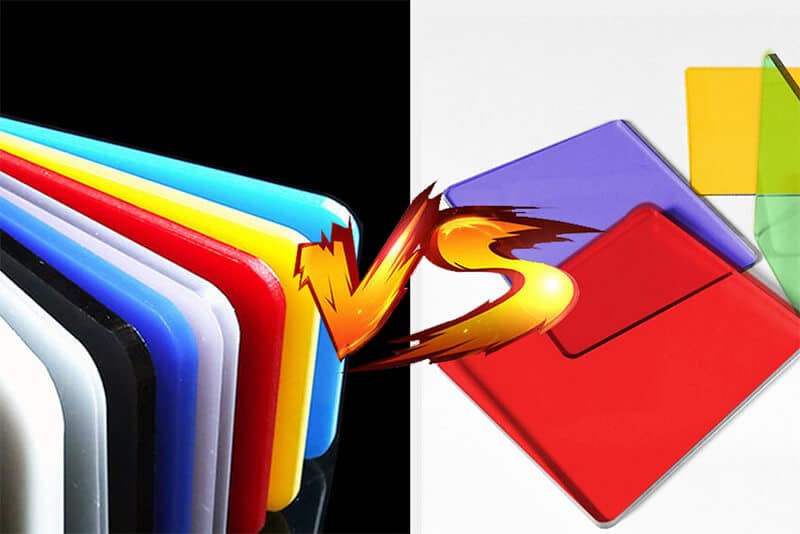
The Ultimate Guide About Acrylic Vs. Polycarbonate

Acrylic’s short form is PMMA. It is a thermoplastic homopolymer. Acrylic is widely used for enhanced weather resistance, durability, and after-use look. On the other hand, Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic polymer. Its short form is “PC”, considered a modern engineering material. This construction material is significantly popular for its exceptional strength, impact resistance, and optical clarity.
Both of these materials are unique in terms of characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, etc. So, product designers, engineers, and professionals must understand the context of Acrylic Vs. Polycarbonate to use the right material. In this article, we provide the ultimate guide about these two construction materials while evaluating their suitability for use.
Acrylic: Everything You Need to Know
Acrylic started its journey in the commercial market in 1933 under the name “Plexiglas.” But its invention happened a long time ago. In 1901, a German chemist named Otto Röhm invented it. Röhm developed the method of polymerization of methyl methacrylate to produce Polymethyl Methacrylate, i.e. Acrylic.
In general, a bulk polymerization process is used to produce PMMA. Within this process, Acrylic is first produced by employing the chemical combination of methyl methacrylate and a catalyst in a mould. Once the combining process is completed, heat is imposed on the mould in a controlled manner. Finally, a chemical transformation takes place within the enclosure, and Acrylic is formed.
Common Characteristics of Acrylic
The following are the base properties of this material.
Common Application of Acrylic
Below are the most common uses of Acrylic.
Advantages of Acrylic
Here, we list the advantages of Acrylic.
Disadvantages of Acrylic
Below are the issues associated with PMMA.
Polycarbonate: Everything You Need to Know
Polycarbonate was initially developed in 1898 by a German chemist named Alfred Einhorn. However, Dr. Hermann Schnell and Dr. Daniel Fox, researchers at the Bayer AG chemical company in Germany, successfully produced Polycarbonate commercially in 1950. Ten years later, in 1960, the General Electric company started producing PR commercially in the USA.
In the process of producing Polycarbonate, bisphenol-A is obtained through the condensation of phenol and acetone under acidic conditions. Then, chemical reactions take place between bisphenol-A and carbonyl chloride in a methyl chloride solvent. In this case, an interfacial procedure takes place.
Common Characteristics of Polycarbonate
Below is a list of the most common properties of Polycarbonate.
Common Applications of Polycarbonate
The following is a list of applications of Polycarbonate.
Advantages of Polycarbonate
Here, we mention the advantages of using Polycarbonate.
Disadvantages of Polycarbonate
The below issues are associated with this material.
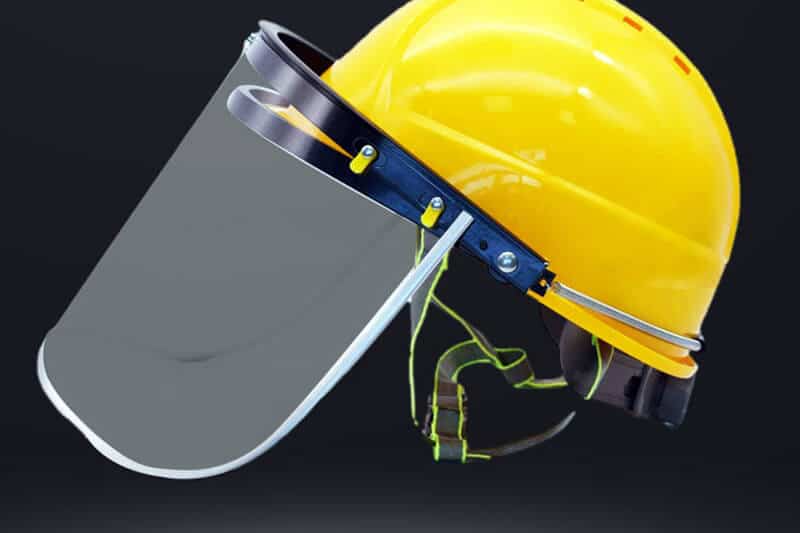
Polycarbonate is a durable and rigid plastic that can withstand chemicals and tear and offers excellent dimensional stability. This material is mainly used to make disposable face shields, laminating, packaging, safety equipment, greenhouse, etc.
Comparison Between Acrylic Vs. Polycarbonate
| Type | Polycarbonate | Acrylic |
|---|---|---|
| Short description | Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic polymer | Acrylic is known as Polymethyl Methacrylate. It is a thermoplastic homopolymer. |
| What ingredients used to make this | Bisphenol-A and carbonyl chloride | Methyl methacrylate, catalyst |
| Applications | Polycarbonate is used to manufacture skylights, domes, greenhouse panels, safety helmets, mobile covers, etc. | Acrylic is used in producing furniture, canopies, lenses, LCD displays, paints, etc. |
| Characteristics | It offers dimension stability and fire resistance properties. It is durable and recyclable. | Impact, weather, and UV resistance. Lightweight. Easy to process. |
| Trade Name | Zelux, Cyrolon, Lexan, Markrolon, etc. | Crylux, Hesalite, Plexiglas, etc. |
| Price | Per Ton Polycarbonate price ranges from $3,100 to $3,830 | Per Ton price is $2,200 to $2,400. |
Final Words
Both Acrylic and polycarbonate are plastics with high light transmittance. But they are different materials with different properties. If you can’t identify them and need a trustworthy supplier, you can choose UVTECO, a leading supplier in China. Contact us for more information about acrylic and polycarbonate.
Related Blogs

Looking for a trustworthy Supplier
Need a Trustworthy Supplier of Plastic, Foam, Sponge, Rubber, Metal, and Machining Solution. Click the Button, We Will Be In Touch With You As Quickly As Possible.